Electricity supply in districts
Energy strategy for showcase district interlinks heating, cooling and electricity
As part of the “Energy Strategy Berlin Adlershof 2020” cluster project, the “Energy Grid Berlin Adlershof” project is aimed at significantly reducing the primary energy requirement at the Adlershof science and technology centre by at least 30 per cent by 2020. The project includes the pilot-like implementation of selected, energy-based concepts and measures that were developed in the “HighTech – LowEx: Energy Efficient Berlin Adlershof 2020” preliminary project.
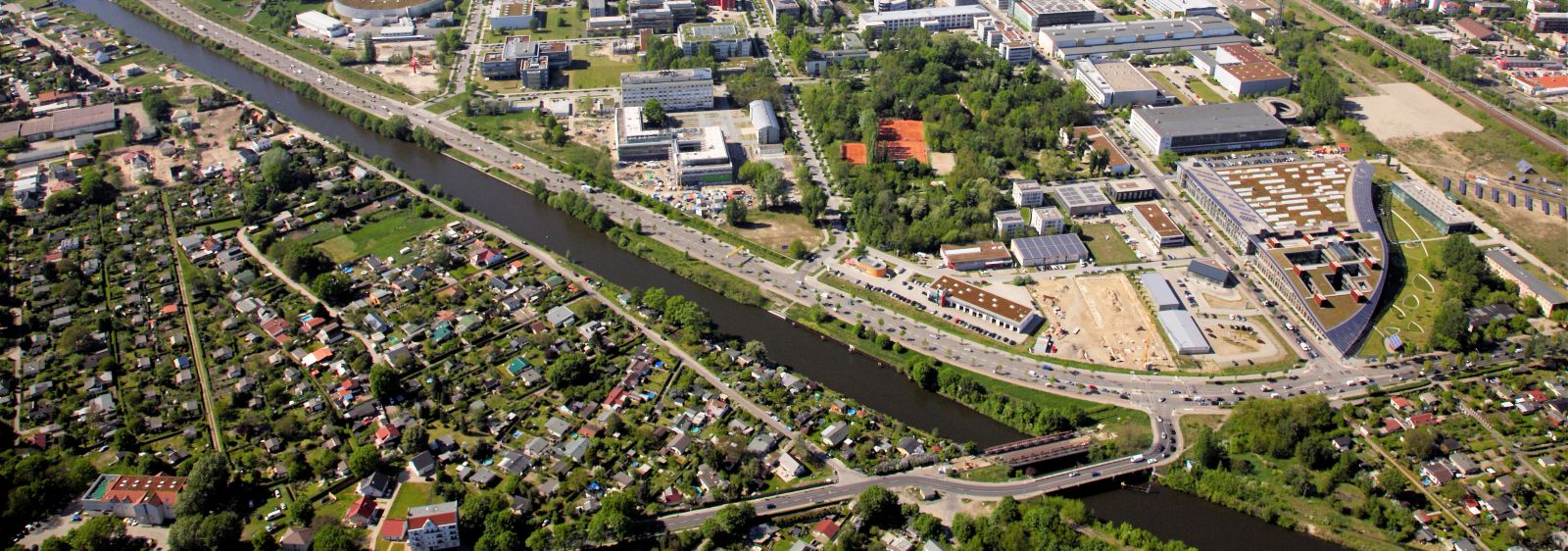
Across an area of 4.2 km2, the Berlin Adlershof high-technology park is home to more than 1,000 companies and scientific institutions whose primary energy requirement has steadily increased in recent years. As part of the "Energy Strategy Berlin Adlershof 2020", the park is now aiming to counter this trend and reduce its primary energy requirement by 30 per cent by the year 2020 relative to the extrapolated trend. Various measures were developed as part of the "HighTech-LowEx: Energy Efficient Adlershof 2020" project that will now be implemented in, for example, the "Energy Grid Berlin Adlershof" project.
The aim is to improve the energy efficiency at the real estate and district level. At the same time, it is also intended to provide planning principles for efficiently supplying urban districts with energy. The project is being implemented as a joint project run by the University of Applied Sciences Berlin (HTW Berlin), SIEMENS AG and the Technische Universität Berlin (TUB), and is being carried out in close coordination with WISTA Management GmbH, Adlershof Facility Management GmbH and various properties on site.
District concept
The three main focus areas of the project encompass the networking of energy flows, a Smart Grid Alliance and the associated energy planning guidelines. The project is primarily aimed at providing a pilot-like representation of an interconnected energy system that encompasses the heating, cooling and electricity energy forms and whose central element is a combined cooling network that links electrically powered cooling systems with renewable cooling generators and storage systems. Based on this supply system, a cross-media energy management system is being designed and implemented in the form of a "Smart Grid Alliance". Based on measurement data from a distributed meter structure, this will derive recommendations for a primary energy efficient operating regime of systems and equipment. In the project, methods and tools for a multi-site set of energy planning guidelines will be developed that adopt the networking concept and thus act as a catalyst for future district planning.
Energy concept
Networking of energy flows
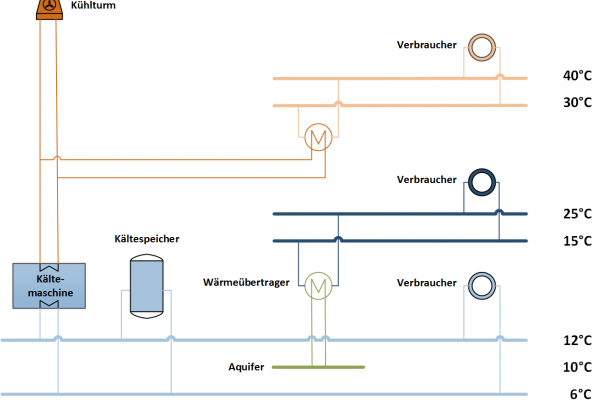
The "networking of energy flows" measure includes the hydraulic optimisation of the existing cooling network, geothermal cooling using an aquifer and the installation of a brine network.
The hydraulic optimisation of the cooling network at the Centre for Photonics and Optics (ZPO) creates the prerequisites for implementing the further measures envisaged. This requires a comprehensive evaluation of the existing systems as well as extensive planning and construction services. This will make it possible to plan the operational processes and design the piping system. As part of a feasibility study conducted by the MegaWATT Ingenieursgesellschaft company, it will also be checked whether a disused ice storage tank system can be refurbished. The cooling network with its generators, loads and the cold storage system will be depicted mathematically to create recommendations for optimising the operating strategy for the network. The realisation of an interconnected network is aimed at enabling a more efficient use of the cooling systems and the optimal integration of a cold storage system and the aquifer.
The geothermal cooling and utilisation of the aquifer requires a detailed, model-based depiction of the storage system and adjacent systems in a simulation environment. This work, which is being conducted by the Technische Universität Berlin, is being supported by the German Research Centre for Geosciences in Potsdam (GFZ). The necessary test drilling is being carried out by DEIG Energietechnik Insumma GmbH. The results of the drilling will then determine whether the measures shall be implemented structurally.
As part of the project, an integrated brine network shall first of all be installed. The Adlershof Technology Park produces significant amounts of waste heat from industrial processes, which are not used owing to the low temperature level. The waste heat can, however, be utilised using hygroscopic salt solutions (brine) that can absorb humidity. Based on the evaluation of the existing systems, it is therefore planned to incorporate heat to generate brine for the network. The focus is on using waste heat from the ZPO’s cooling system and on connecting the brine regeneration to the planned aquifer. In addition, a greenhouse, which will be used as a humid air collector, shall also be connected to the brine network. A demonstration pavilion is being built on the Adlershof campus for this purpose, which has been designed and implemented by the Technische Universität Berlin as part of a Climate-KIC project funded by the EU.
Smart Grid Alliance
The aim of this measure is to test a smart grid on the campus that utilises electricity, heat and cooling energy media and is exemplary for Germany’s energy transition. It is intended that the "Adlershof Smart Grid Alliance" interest pool will make a decisive contribution to its implementation. It encompasses properties which, in terms of their load shifting potential and savings possibilities, are suitable for participating in the construction of the smart grid. The aim is to achieve a model-based depiction of a smart grid by incorporating their specific energy flows. Based on measurement data, the ecological and economic benefits shall be assessed and valued. These findings will form the basis for a medium-term implementation of the smart grid on campus.
The "Energy supply networks and the integration of renewable energies" (SENSE) department at the Technische Universität Berlin has primary responsibility for developing the Smart Grid Alliance.
The establishment of the Smart Grid Alliance requires the comprehensive integration of different players. The necessary communication activities are being carried out by the Centre for Technology and Society (ZTG) at the Technical University of Berlin. At the same time, it is also investigating influencing factors and the acceptance of the measures being implemented by the Smart Grid Alliance.
Energy planning guidelines
The energy planning guidelines are aimed at planning how future energy needs can be met in urban development terms, whereby the guidelines link energy supply systems (supply) with the traditional land-use and development planning (demand) used by local authorities. The starting point is provided by the district-based, energy efficiency target of reducing the primary energy requirement at the Adlershof site by 30 % by 2020. Taking into account the existing and planned energy networks, and building on the usage typology and urban planning typology derived from the previous "HighTech – LowEx: Energy Efficient Berlin Adlershof 2020" project, exemplary usage and functional variants will be developed and evaluated in energy efficiency terms. Successive scenarios for creating an energy-efficient Adlershof science quarter will incorporate the whole area designated for urban development measures, i.e. it will include areas that are still undeveloped. The planned energy developments will be depicted in the resulting energy usage plan. The "Energy Grid Berlin Adlershof" project represents the first time that the energy planning guidelines method, which was first developed in Bavaria for smaller residential areas, has been applied and accordingly developed in an inner-city commercial and technology district.
Research
HTW Hochschule für Technik und Wirtschaft Berlin, FB I Regenerative Energien
http://regenerative-energien.htw-berlin.de/
susanne.rexroth@htw-berlin.de
Research
Siemens AG
http://www.siemens.com
cornelia.petermann@siemens.com